The Dividend Discount Model (DDM): The Black Sheep of Valuation?
Brian DeChesare
MAY 3, 2023
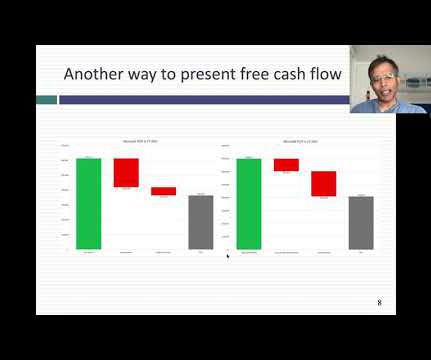
When I started offering financial modeling training , I never expected to get questions about a methodology like the Dividend Discount Model (DDM). Otherwise, the written version follows: Why Use a Dividend Discount Model? The main argument in favor of the DDM is that it best represents what happens in real life when you buy a stock.





















Let's personalize your content